Repeaters, Bridges, Routers, and Gateways
Network Repeater
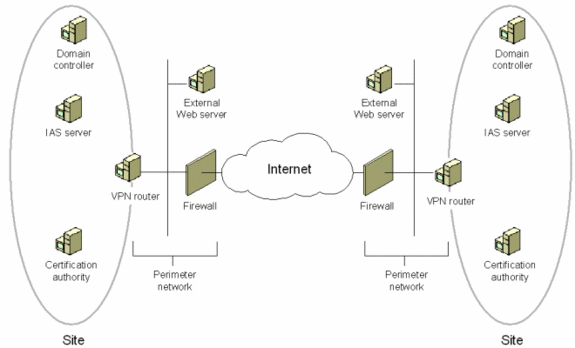
A repeater connects two segments of your network cable. It retimes and regenerates the signals to proper amplitudes and sends them to the other segments. When talking about, ethernet topology, you are probably talking about using a hub as a repeater. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network communication when there are several repeaters in a row. Many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row. Repeaters work only at the physical layer of the OSI network model.
Bridge
A bridge reads the outermost section of data on the data packet, to tell where the message is going. It reduces the traffic on other network segments, since it does not send all packets. Bridges can be programmed to reject packets from particular networks. Bridging occurs at the data link layer of the OSI model, which means the bridge cannot read IP addresses, but only the outermost hardware address of the packet. In our case the bridge can read the ethernet data which gives the hardware address of the destination address, not the IP address. Bridges forward all broadcast messages. Only a special bridge called a translation bridge will allow two networks of different architectures to be connected. Bridges do not normally allow connection of networks with different architectures. The hardware address is also called the MAC (media access control) address. To determine the network segment a MAC address belongs to, bridges use one of:
- Transparent Bridging - They build a table of addresses (bridging table) as they receive packets. If the address is not in the bridging table, the packet is forwarded to all segments other than the one it came from. This type of bridge is used on ethernet networks.
- Source route bridging - The source computer provides path information inside the packet. This is used on Token Ring networks.
Network Router
A router is used to route data packets between two networks. It reads the information in each packet to tell where it is going. If it is destined for an immediate network it has access to, it will strip the outer packet, readdress the packet to the proper ethernet address, and transmit it on that network. If it is destined for another network and must be sent to another router, it will re-package the outer packet to be received by the next router and send it to the next router. The section on routing explains the theory behind this and how routing tables are used to help determine packet destinations. Routing occurs at the network layer of the OSI model. They can connect networks with different architectures such as Token Ring and Ethernet. Although they can transform information at the data link level, routers cannot transform information from one data format such as TCP/IP to another such as IPX/SPX. Routers do not send broadcast packets or corrupted packets. If the routing table does not indicate the proper address of a packet, the packet is discarded.
Brouter
There is a device called a brouter which will function similar to a bridge for network transport protocols that are not routable, and will function as a router for routable protocols. It functions at the network and data link layers of the OSI network model.
Gateway
A gateway can translate information between different network data formats or network architectures. It can translate TCP/IP to AppleTalk so computers supporting TCP/IP can communicate with Apple brand computers. Most gateways operate at the application layer, but can operate at the network or session layer of the OSI model. Gateways will start at the lower level and strip information until it gets to the required level and repackage the information and work its way back toward the hardware layer of the OSI model. To confuse issues, when talking about a router that is used to interface to another network,the word gateway is often used. This does not mean the routing machine is a gateway as defined here, although it could be.